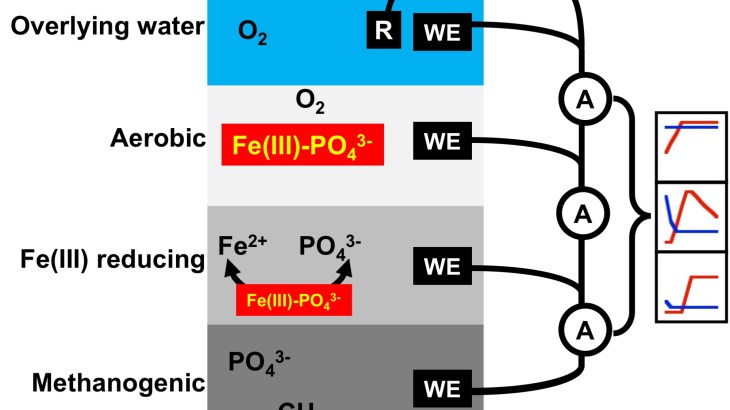
Release of phosphate-P immobilized in benthic sediments poses a remnant threat to induce harmful algal blooms (HAB) despite adequate management of external loads of phosphate. This process, referred to as internal loading of P, is induced by microbially mediated alternations of sediment and porewater chemistry and bacteria that “breath” iron are mostly responsible for controlling the release of P from sediments. We have developed an electrochemical split-chamber zero resistance ammetry (SC-ZRA) technique that we can use to detect microbiological activities.