
Related to organizational behavior and human resource management, several ongoing research projects. Students will be involved in various aspects of the project, including design, data collection, and analysis.

Related to organizational behavior and human resource management, several ongoing research projects. Students will be involved in various aspects of the project, including design, data collection, and analysis.

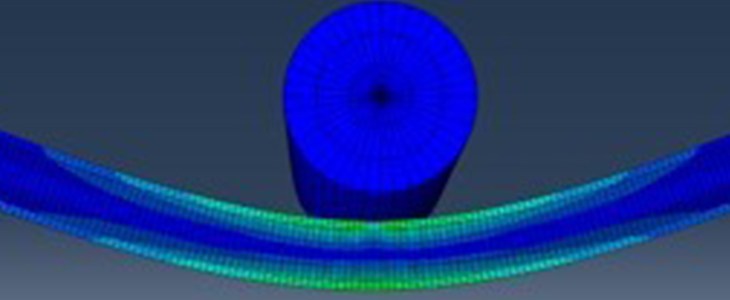
Composite materials are commonly employed in modern aircraft structures and in many aerospace applications like engine casing, fan-blades, etc. This is attributed to their high strength-weight ratio and high stiffness-weight ratio, making composites extremely light, yet exceptionally strong. However, the use of composites makes them susceptible to damage, which could result in complex failure mechanisms like delamination, matrix cracking, fiber debonding, fiber fracture, etc.
The concept of biomimicry is solving problems and creating new opportunities through understanding and applying biological models. Very often, innovation inspired by nature and careful examination of the natural world are potential ways to seek solution to real-world problems. In this project, students will conduct experimental testing and computational analysis at Prof. K.T. Tan’s Advanced Metacomposites Laboratory to investigate the amazing structure of biological models.
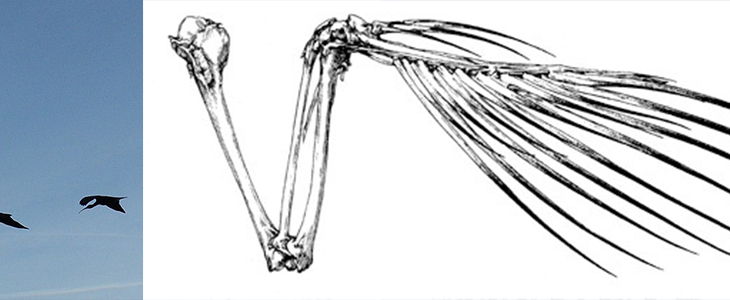
In this project, students will conduct experimental testing and computational analysis at Prof. K.T. Tan’s Advanced Metacomposites Laboratory to investigate the amazing bone structure of biological models with flight capability.
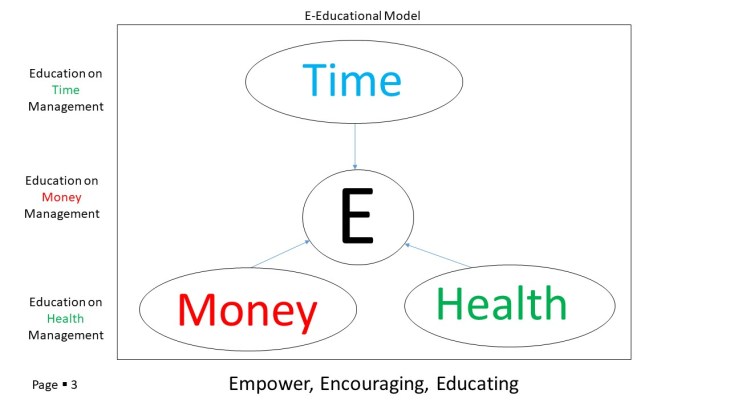
The researchers use time, money and health as the basic individual/family resources to education university community to rethink the resources and survive the pandemic period.

Lightweight, composite sandwich panels are being increasingly used in navy combat ships, but not much is known of their behavior at Arctic temperatures. Project explores crushable behavior and energy absorption of PVC foam at temperatures as low as -60 deg C.
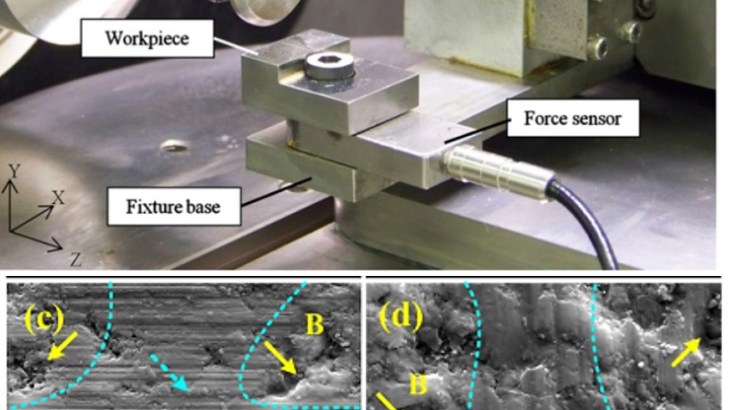
The grinding of brittle materials, such as ceramics, presents several unique challenges not found in the grinding of metals. Among these challenges are the use of diamond abrasives, the dressing of grinding wheels, a tendency towards higher specific energies, and the tendency of the workpiece to crack under grinding.

The Personal Growth & Methods Lab engages in various projects related to one of three areas: personal growth, international student well-being, and data collection methodology. We are currently recruiting students to assist with projects related to the relationships among gender, empowerment, and personal growth.
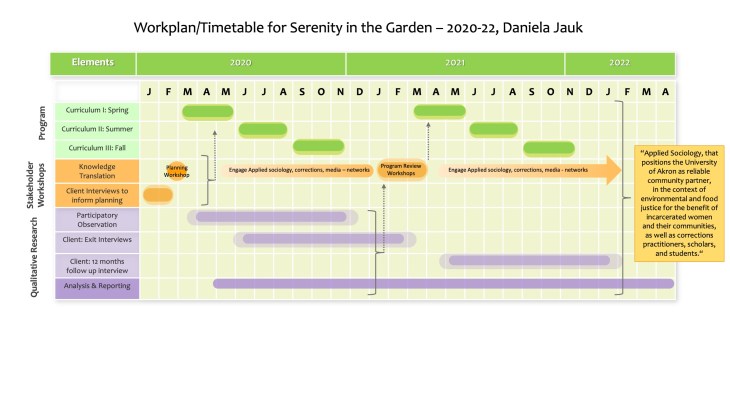
The aim of this local pilot-study is to further develop and qualitatively assess an educational gardening program for incarcerated women in Northeast Ohio. This is part of a larger project that started in Spring of 2019 and will continue until 2021.

This service-learning project will be conducted by The University of Akron coordinators of Service-Learning and will work with the local Enterprise branch and local United Ways.
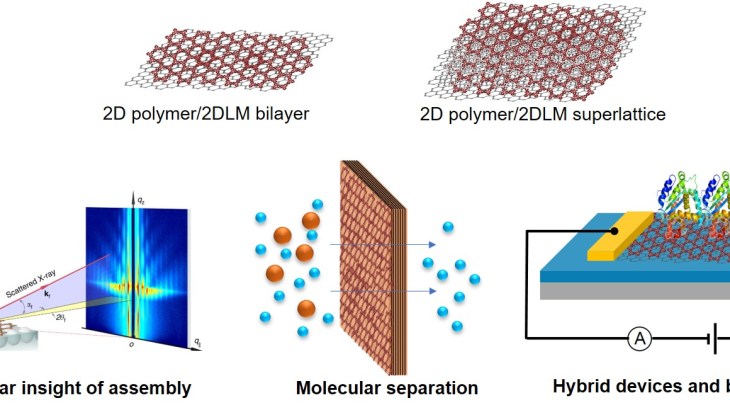
Graphene, boron nitride, dichalcogenides and other inorganic 2D layered materials (2DLM) have atomically thin structure with unique electrical, mechanical, thermal, and optical properties, and have already been extensively explored for electronics, sensing, catalysis and biomedical applications. On the other hand, in the polymer world, there is an emerging class of 2D polymers with analog structure to 2D layered materials.
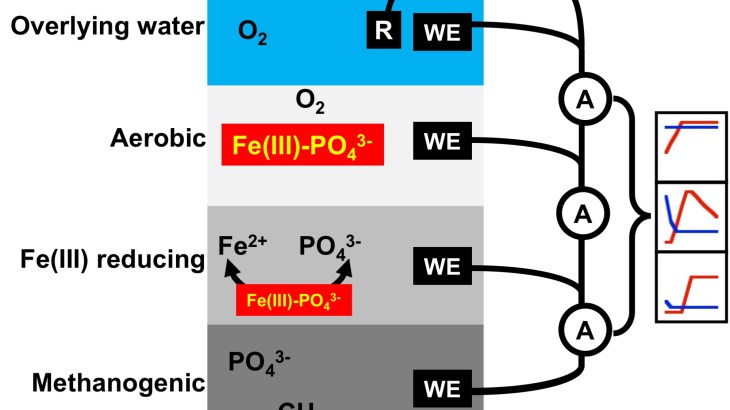
Release of phosphate-P immobilized in benthic sediments poses a remnant threat to induce harmful algal blooms (HAB) despite adequate management of external loads of phosphate. This process, referred to as internal loading of P, is induced by microbially mediated alternations of sediment and porewater chemistry and bacteria that “breath” iron are mostly responsible for controlling the release of P from sediments. We have developed an electrochemical split-chamber zero resistance ammetry (SC-ZRA) technique that we can use to detect microbiological activities.

Soft particle glasses (SPGs) are composed of elastic non-Brownian particles that are jammed beyond the packing fraction of equivalent hard spheres. SPGs show solid-like behavior at rest, and they flow when subjected to external stimuli such as shear deformation. Considering this tunable rheological property, they have been used as additives in many products such as cosmetic creams, hair gels, food products, paper coating industries, and recently it has been suggested that these suspensions can be used in the drilling muds.

The goal of this project is to document the perceptions and experiences with health, health care and interpersonal violence among female former prison inmates. Successful reentry of former inmates into society remains an important goal for community, healthcare, and criminal justice professionals. An important component of reintegration is assessing health, health care and interpersonal violence experiences among inmates during and after release from prison.

This study will collect and analyze data on the experiences of our campus community, focusing on mental health, well-being, and how these affect student’s academic performance and persistence. Online surveys will be conducted in the fall semesters for three years (2019-2021) on a sample of students, faculty and staff. The 2019 student survey has completed. Data are ready for analysis.

Our group has developed a rheological apparatus capable of sustaining spatial thermal gradients in shear rheometry. It is hypothesized that orthogonally superimposed thermal fields will produce linear, field-averaged rheological responses up to a threshold where anomalous, thermo-rheological dissipative phenomena will occur. The molecular influence of heat flow, especially at reduced dimensions, is from entropy production.

Our group has recently discovered a material system that potentially may have elastomeric properties. The Internation Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines an elastomer as a polymer that displays rubber-like elasticity, i.e. high viscoelasticity with weak intermolecular forces. We are seeking a highly motivated and ambitious student to assist us in exploring this material system for its potential elastomeric properties and to help us elucidate the rational design of such a material system through characterization of the material properties of various molecular constructs.

Peer mentors/research assistants are sought for the PULSe program. Those with ASD have particular modes of thinking and learning that is outside the realm of standard pedagogical practices. In the proper environment, these modes may help those with ASD to flourish. However, they are normally disadvantaged in basic learning environments. Academia is not wholly equipped to instill and help develop the necessary tools for ASD students to effectively function in society. Our aim is to bridge the learning gap.

Our group has developed a rheological apparatus capable of sustaining spatial thermal gradients in shear rheometry. It is hypothesized that orthogonally superimposed thermal fields will produce linear, field-averaged rheological responses up to a threshold where anomalous, thermo-rheological dissipative phenomena will occur. The molecular influence of heat flow, especially at reduced dimensions, is from entropy production. Translational and orientational motions evolve as a molecular compensation mechanism.

Helicenes are polycyclic aromatic compounds which are formed by ortho-fused aromatic rings that generate a non-planar, screw-shaped, three-dimensional structure that is inherently chiral and spring-like. The helical topology significantly contributes to the emergent properties of helicenes and has been garnering interest in the fields of nanotechnology, macromolecular and materials science.
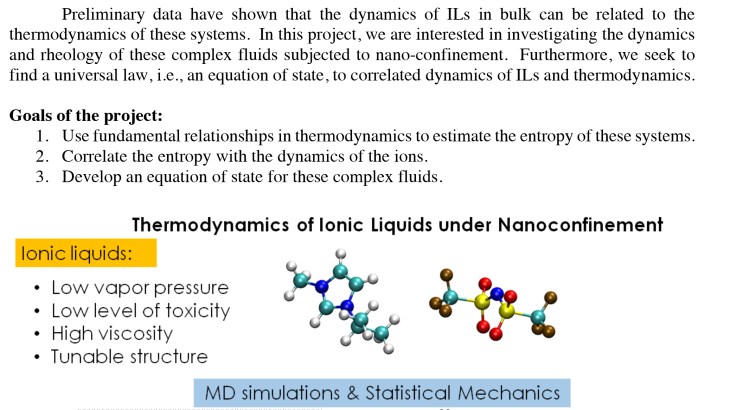
Ionic liquids (ILs) are defined as salts that melt at or below 373 K. A typical IL is composed of a bulky organic cation and an inorganic or organic anion. As a group, many ILs tend to be miscible with many organic solvents. They show low vapor pressure, high viscosity and low degree of toxicity. At low temperatures ILs do not crystallize; instead, they form a glassy phase, while at high temperatures they flow with high viscosity, which is due to the strong electrostatic interactions between cations and anions.
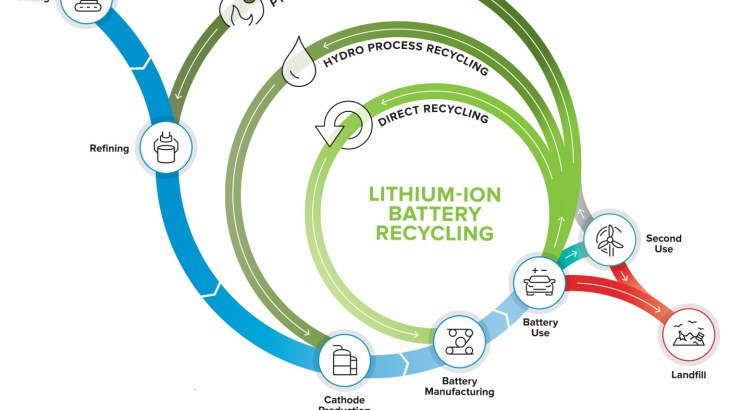
Manufacturing new energy systems such as fuel cells, batteries, wind turbines, photovoltaic cells, and catalytic reactors require materials that may be (1) precious, (2) rare on the earth, (3) not available or easily accessible in the United States, and/or (4) harmful for environment. Therefore, recycling (separation and reusing) energy materials is important.

The Early Modern Recipes Online Collective (EMROC) is a long-term project looks to include scholars, students and the general public in the preservation, transcription and analysis of recipes written in English from circa 1550-1800. The ultimate goal is an accessible and searchable corpus of recipe books currently in manuscript.
This project looks to design new corrosion inhibitors through experimentation and computer-aided design. The undergraduate student will work with a graduate student, assisting them in performing experiments on various systems and in the computer-aided design aspects of the project.
Plastic waste recycling is plagued by imperfect sorting processes which leaves recycling feeds contaminated with polymers of different molecular composition. These blends have thermodynamic driving forces to phase separate and entropic forces which produce weak interfaces between the materials.

Study is to investigate the effect of professional development participation on Head Start teachers’ growth related to Phonemic Awareness (PA) instructional knowledge and skills.

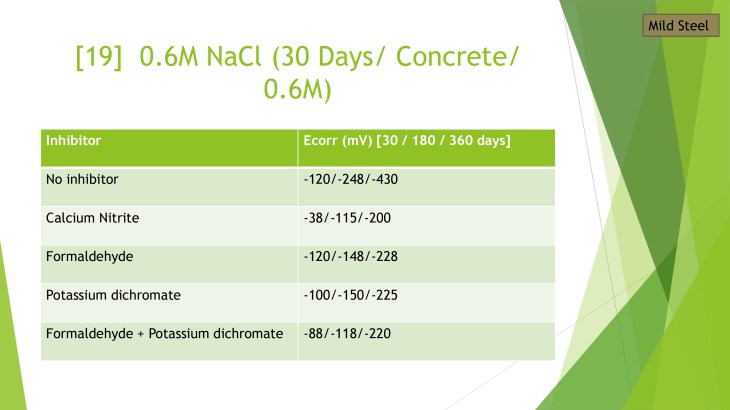
This project aims to investigate the effect of soluble salts on the failure of coatings. The corrosion resistance and adhesion of the coating will be studied to understand the influence of soluble salts.

This project aims to investigate the effect of pigments on the properties of coatings. The high-performance pigments are expected to improve the coating’s corrosion resistance and UV stability.

This project aims to develop a new biobased coating from substaniable resources. The coating is expected to be comparable to the petroleum based coating.

This project aims to develop a new approach to generate polyurethane coating without using isocyanates, which are very toxic materials. The non-isocyanate polyurethane is expected to behave similar to the traditional isocyanate-based polyurethane.

This project aims to develop a “cool” coating by invorporating inorganic pigments that reflect near-infrared radiation (NIR) into a commercial coating matrix.

Psychotherapy process and outcome variables; Applied psychology experiences; Undergraduate student success; Infusing diversity and social justice material into classrooms.

Looking for a few good students to work on a research project. We need some dedicated students to help administer a lab study that we hope to run soon.

General Research Interest: I/O Psychology. Current Undergraduate Opportunities: Data Collection, Data coding, Data cleaning, Experimental Facilitating.

Research program focuses primarily on career development with a particular interest in the ways in which culture and social identities influence interests, choices, leadership, and educational and career outcomes.

Compiling and summarizing literature & data entry, time commitment: 1-2 hours a week. Current Number of Openings: 1

Understanding Motivation and Emotions in Call Center Work (Laboratory Simulation; Field Research at a Call Center Organization). Current Undergraduate Opportunities: Assisting in all phases of the research process.

Examining the relationship between benevolent ageism and gender on mental health outcomes in older adults; how minority stress (outness and internalized homophobia) in same-sex couples influences sexual and relationship satisfaction; how to teach about diversity topics at the college level; experiences of discrimination and acculturation in a lifespan sample of Bhutanese refugees.

This project entails developing plant based vaccines using smart genomics. Vaccines are essential for protecting all segments of the civilian population from pandemic influenza to other emerging infectious diseases.

We are preparing and publishing scholarly editions of texts found in nineteenth-century Ohio magazines and newspapers. Volumes are published electronically and in print.
The project consists of designing and fabricating photo-programmable microstructures consist of microfluidic ecosystem and interacting biological species. The biohybrid system exploits power, sensing and navigation of the biological components and the sensivity of the photo-active parts to tune the dynamics of species within the micro-ecosystem.
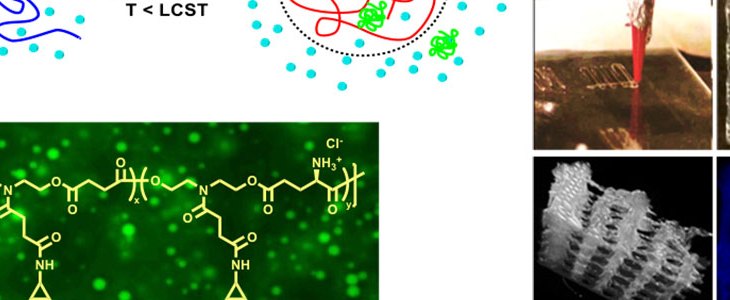
The Joy Lab has developed a platform of polyesters and polyurethanes that are being utilized for the incorporation and sustained delivery of therapeutics. The undergraduate student working on the project will work specifically towards the synthesis of the polymers, incorporation of the therapeutic within the polymer and analyze the release kinetics. The student will gain experience in synthesis and characterization of polymers and in the analysis and interpretation of experimental data.

The purpose of this study is to develop a novel double network hydrogel that will be able to exhibit greater mechanical properties to become more applicable in the medical field will help to explore fundamental understanding about the double network hydrogel and materials to create it for future development.
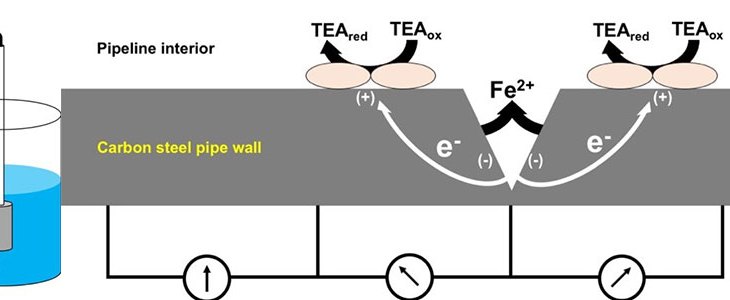
There are over 300,000 miles of natural gas transmission pipeline in the US (Pipeline 101 see web addresses; P&GJ paper 2016). To meet the growing need to transport shale gas in the US, approximately 3,400 miles of new gas pipeline were constructed in 2015-2017 (ferc.gov), and that trend is likely to continue, as the US continues to develop as a major natural gas and petroleum exporter.
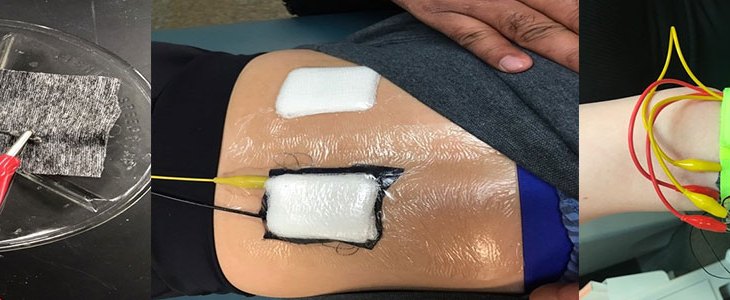
Our team has developed flexible, lightweight fabric materials that can selectively determine physiological information from sweat forming on the surface of the skin. The technology is the first lightweight fabric sensor to provide real-time information regarding hydration levels during exercise or training through selective determination of sodium ion levels.
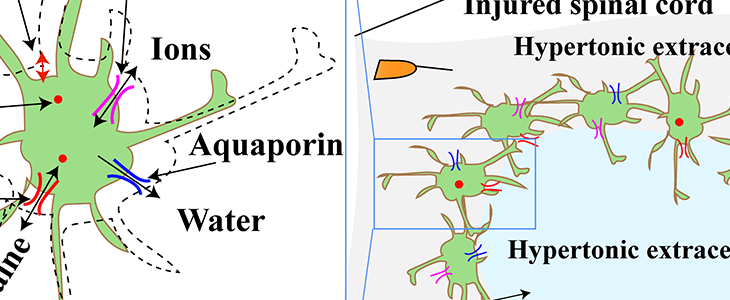
Employing an in vitro swelling assay, cell volume will be assessed after manipulating CHDH and BGT-1 activity in hypertonic conditions to examine the direction of the fluid transport through the cell membrane by live imaging using confocal microscopy followed by analytical quantification of betaine.

What is the osmolality of CSF, extracellular fluid (ECF), fluid from syrinx in syringomyelia/PTSM rats? The fluids mentioned above will be harvested from the rats having syringomyelia, the osmolality of those fluids will be determined using osmometer. The study of osmolality of fluids will explain the potential syrinx formation/expansion mechanism.
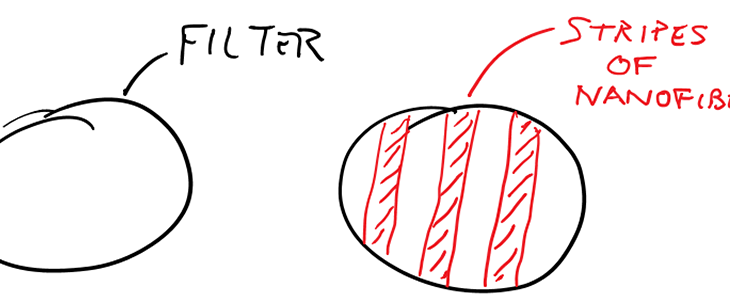
Nanofibers have different wetting properties than glass fibers used in common filter media. Recent works with modifying surface properties of filter media shows non-wetting chemical coatings applied in striped patterns can improve performance of coalescing filters. The hypothesis for this work is the nanofibers which enhance wetting properties and droplet capture will similary improve filter performance if applied in striped patterns.
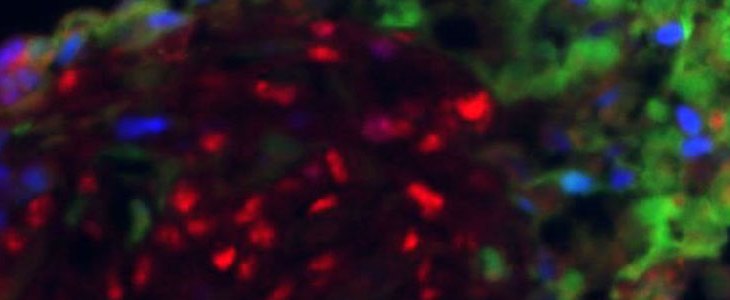
We use a bioengineering approach to develop biomimetic three-dimensional tumor models to understand the disease biology and test and identify novel treatments. We are an interdisciplinary team of graduate and undergraduate students tackling a very significant problem using a combination of biomedical and biological approaches.

Pyrolyzed (process of low or no oxygen thermal decomposition –carbonization- to convert biomass into clean and renewable carbon products) biomass obtained from agricultural products such as soybean hulls, sorghum etc., is used as a renewable, low cost and eco-friendly material which has large potential for reinforcement or functionality-inducing (such as electrical, thermal conductivity) filler for polymeric materials.
The formation of polymer networks inevitably introduces topological defects, such as loops. While these defects undermine the mechanical properties of the materials, they could also bring opportunities for the design of new materials.

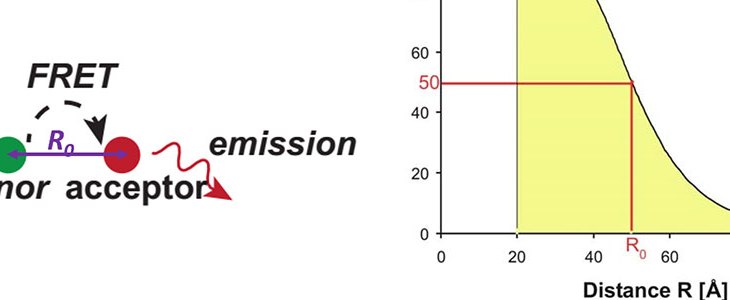
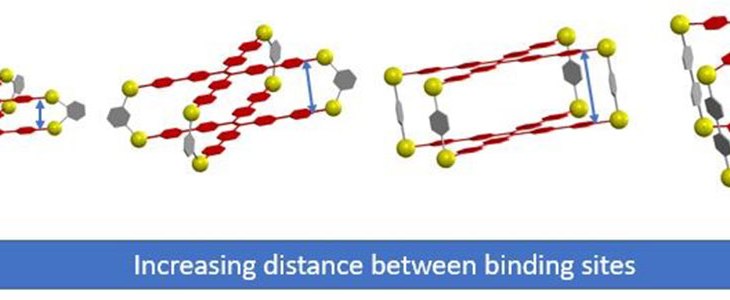
Controlling and measuring the intermolecular distance in supramolecular structures are important as well as challenaging. To achive both at the same time, we are chemically incorporating an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) luminophore into a charged macromoleculre, which can self-assemble into stable supramolecular structures of different intermolecular distances through the careful regulation of the physical interactions between the building blocks.
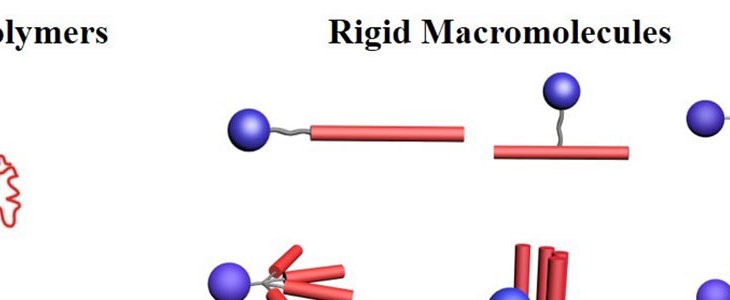
The participants will have experience on the synthesis of macromolecules and several advanced characterization techniques such as light scattering, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscope (AFM), etc.
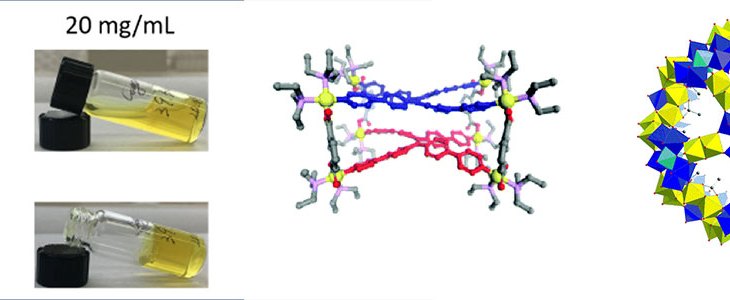
Hydrogel, conventionally defined as networks held up by cross-links and entrapping solvent in intermolecular spaces, has been widely used in clinic trials. Understanding the formation mechanism will be helpful to develop new materials.
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) has received great attention since AIE makes it possible to actively utilize the aggregation process, which against the well-known aggregation-caused quench (ACQ).
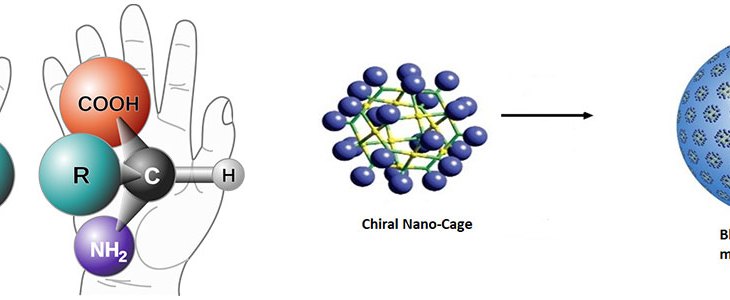
In our group, we use chiral nano-cages as simple models to explore what has happened during the early stages of life led to “homochirality” phenomena.
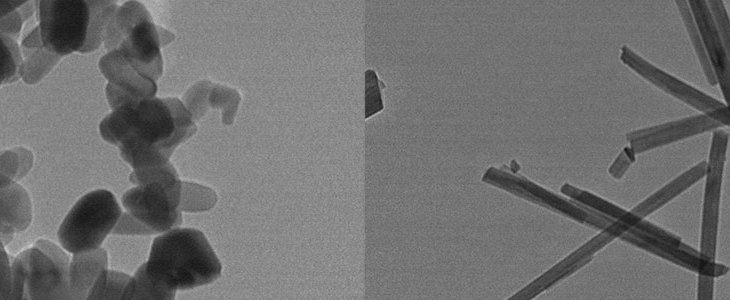
Nanoparticles (NPs) are used widely in cosmetics and for drug delivery and thus come in contact with blood and other fluids in the body. NPs present in biological fluids rapidly interact with proteins, which undergo structural changes upon binding to the NPs. These conformational (structural) changes of the protein determine the biological responses of the NPs in the living system.
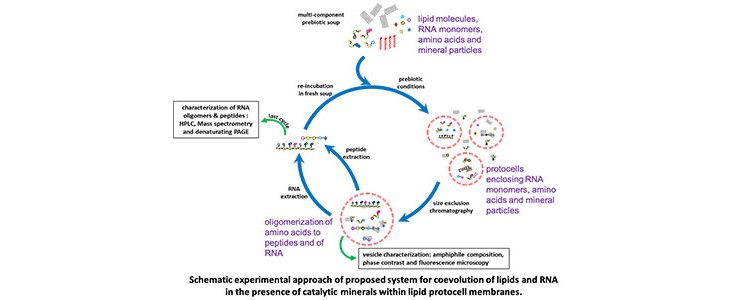
The Earth is about 4.56 billion years old and the earliest evidence of life is at approximately 3.8 billion years ago. How life originated from a planet composed of only minerals, dissolved elements, and simple organic molecules is one of the great questions of scientific inquiry. Life requires complex biomolecules, such as proteins, RNA and DNA, to maintain a cell and for reproduction.
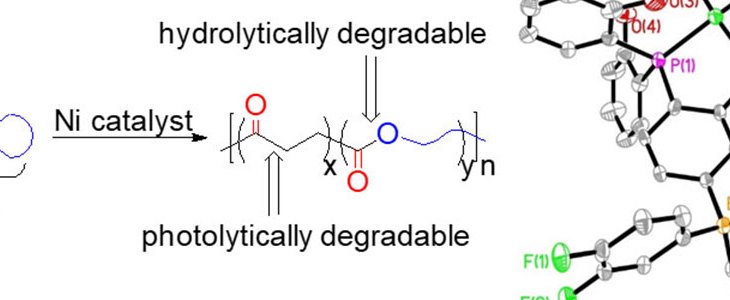
“White pollution” is a problem of massive scale. To replace the current nondegradable commodity plastics with degradable plastics, a key challenge is that the new raw materials must be readily available at costs comparable to current monomers such as ethylene and propylene. Low-carbon footprint is highly desirable for these raw materials in order to achieve overall environmental sustainability.
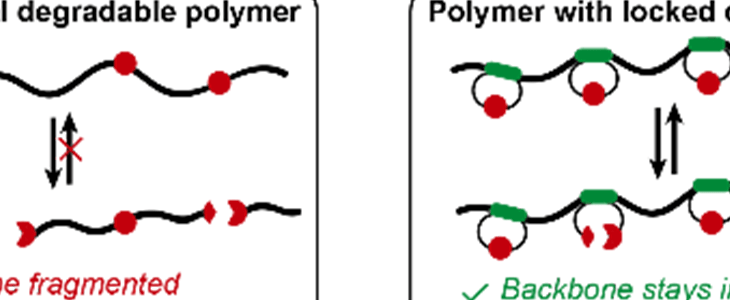
Synthetic degradable polymers are of pivotal importance for recycling and sustainability. While the degradability allows polymers to be recycled, it can also cause stability issue, which impairs the storage and functioning of materials.
Understanding the physical and chemical interactions between ice and materials is of interest in order to tune adhesion and friction on ice to meet various material demands. For example, it is important for tires to have good traction on ice and snow, and low ice adhesion coatings are needed for applications on aircraft, power lines, wind turbines, and costal structures/ships. This project aims to find specific material surface properties in nature that have been evolved to either increase or decrease ice nucleation, adhesion, and/or friction.
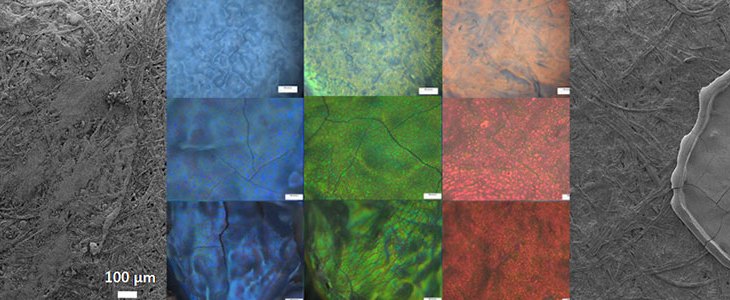
Structural color-based printing inks possesses several advantages to conventional pigmentary inks in terms of color perpetuity and cost effectiveness. However, there are certain challenges while using these structural color systems.
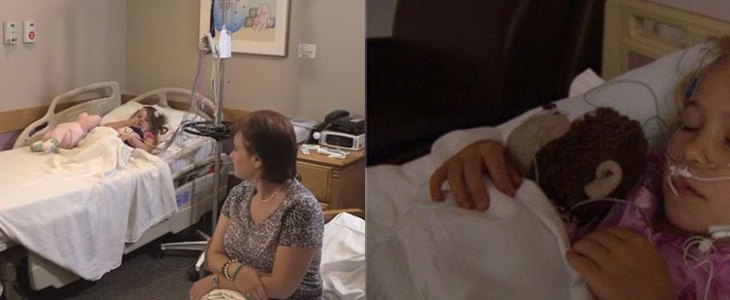
This project involves current work with Akron Children’s Hospital (ACH), and entails finding new and cost-effective ways of diagnosing pediatric sleep apnea using new tools such as low-cost Arduino micro-processors, new low-cost sensors, wireless technology, advanced signal procssing algorithms such Wavelets, etc. Selected students will work within a research group and may be onboarded at ACH so that they can help in clinical tests at the hospital.

The project will focus on the 3D printed polymer electrolyte and related lithium ion battery components.
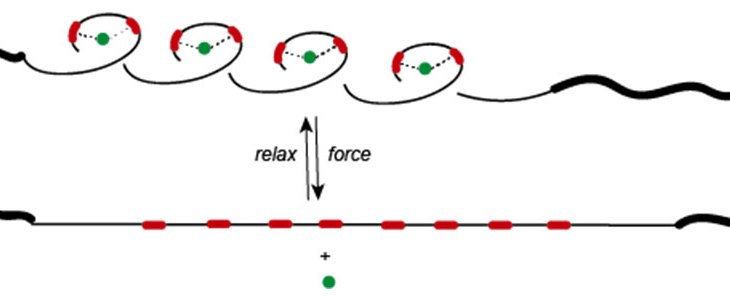
Mechanical stress is ubiquitously present in materials and biological systems, and the force-induced bond scission and materials failure have been extensively studied. In recent years, utilizing mechanical force to do targeted and constructive chemistry, largely fueled by the concept of mechanophore, i.e., stress-responsive moiety, has become a new trend.

There are a variety of material and testing concepts being pursued for high temperature, extreme environments with stress for a number of advanced materials (high temperature ceramic composites and coatings) research projects.

Interaction of shock wave with boundary layer (SWBL) cause possible formation of recirculation zone and larger-scale zone of influence upstream and downstream of the point of the incident shock wave. These aerodynamic phenomena affect the shear and pressure forces acting on the surface, aerodynamic resistance and aerodynamic heating of propulsive systems and supersonic air vehicles.